
The Rover P6 series (named as the 2000, 2200, or 3500, depending on engine displacement) was a saloon car produced by Rover and subsequently British Leyland from 1963 to 1977 in Solihull, West Midlands, England, UK.
The P6 was the first winner of the European Car of the Year award.
The P6 was announced on 9 October 1963, just before the Earls Court Motor Show.
The vehicle was marketed first as the Rover 2000 and was a complete "clean sheet" design intended to appeal to a larger number of buyers than earlier models such as the P4 it replaced. Rover had identified a developing market between the standard '1.5-litre' saloon car class (such as the Ford Consul and the Singer Gazelle) and the accepted 'three-litre' large saloon cars (typified by the Wolseley 6/99 and the Vauxhall Cresta). Younger and increasingly affluent professional workers and executives were seeking out cars that were superior to the normal 1.5-litre models in style, design and luxury but which offered more modern driving dynamics than the big three-litre class and lower purchase and running costs than sports saloons such as the Jaguar Mark 2. Automotive technology had improved significantly in the mid-to-late 1950s, typified by the introduction of cars such as the Citroen DS and Lancia Flavia in Europe and the Chevrolet Corvair in America. The replacement for the traditionally-designed P4 would therefore be a smaller car with a two-litre engine (although a gas turbine was envisioned as power unit in the future) utilising the latest design, engineering and styling, thus making the Rover one of the earliest examples of what would now be classified as an executive car. The P6 would be lower-priced than the P4 and sales volumes were anticipated to be significantly higher. The more upmarket and conservative P5 was sold alongside the P6 until 1973.

Rover T4 gas turbine prototype (1961)
The 2000 was advanced for the time with a de Dion tube suspension at the rear, four-wheel disc brakes (inboard on the rear), and a fully synchromesh transmission. The unibody design featured non-stressed panels bolted to a unit frame, inspired by the Citroën DS. The de Dion set-up was unique in that the "tube" was in two parts that could telescope, thereby avoiding the need for sliding splines in the drive shafts, with consequent stiction under drive or braking torque, while still keeping the wheels vertical and parallel in relation to the body.
The Rover 2000 won industry awards for safety when it was introduced and included a carefully designed "safety" interior. One innovative feature was the prism of plastic on the top of the front side lights. This allowed the driver to see the front corner of the car in low light conditions, and also confirmed that they were operative. The relatively sharp plastic projections did not meet homologation standards in some export markets, including Germany, however and so a lens with a smooth top was substituted where the law demanded.
One unique feature of the Rover 2000 was the design of the front suspension system, in which a bell crank (an L-shaped rotating bracket trailing the upper hub carrier joint) conveyed the vertical motion of the wheel to a fore-and-aft-horizontally mounted spring fastened to the rear wall of the engine compartment. A single hydraulically damped arm was mounted on the bulkhead for the steering. The front suspension was designed to allow as much width for the engine compartment as possible so that Rover's gas turbine engine could be fitted. The styling outline was first seen in the 1961 prototype T4, a front-engined front-wheel-drive gas turbine saloon, one of a line of gas turbine prototypes built by Rover in the 1950s and 1960s.
T4 survives today and can be seen at the British Motor Museum.
In the event, the gas turbine engine was never used for the production vehicle, but the engine compartment width (with slightly amended shape) did facilitate the accommodation of the Buick-derived Rover V8 engine made available in the P6 from April 1968.

The Citroën DS19 inspired the Rover 2000 design
Sculptor Flaminio Bertoni's Citroën DS body inspired David Bache. With a nod to the new Kamm tail, the finished Rover appearance incorporated a necessarily enlarged boot filled otherwise by Rover's de Dion rear suspension. It lacked the Citroën shark nose, which it was planned to introduce later as a drooping bonnet with headlamps in pods and projecting sidelights.
Luggage compartment space was limited due to the complex rear suspension and, in Series II vehicles, the boot mounted battery. The spare wheel competed for space also, and was stored either flat on the boot floor or vertically to the side. A later optional 'touring package' allowed the spare to be carried on the boot lid; with a vinyl weatherproof cover. When not in place, the mounting bracket was concealed by a circular Rover badge. Series II models briefly offered Dunlop Denovo Run-flat tyre, eliminating the need for a spare, though this was not commonly selected and is very unusual on surviving examples.

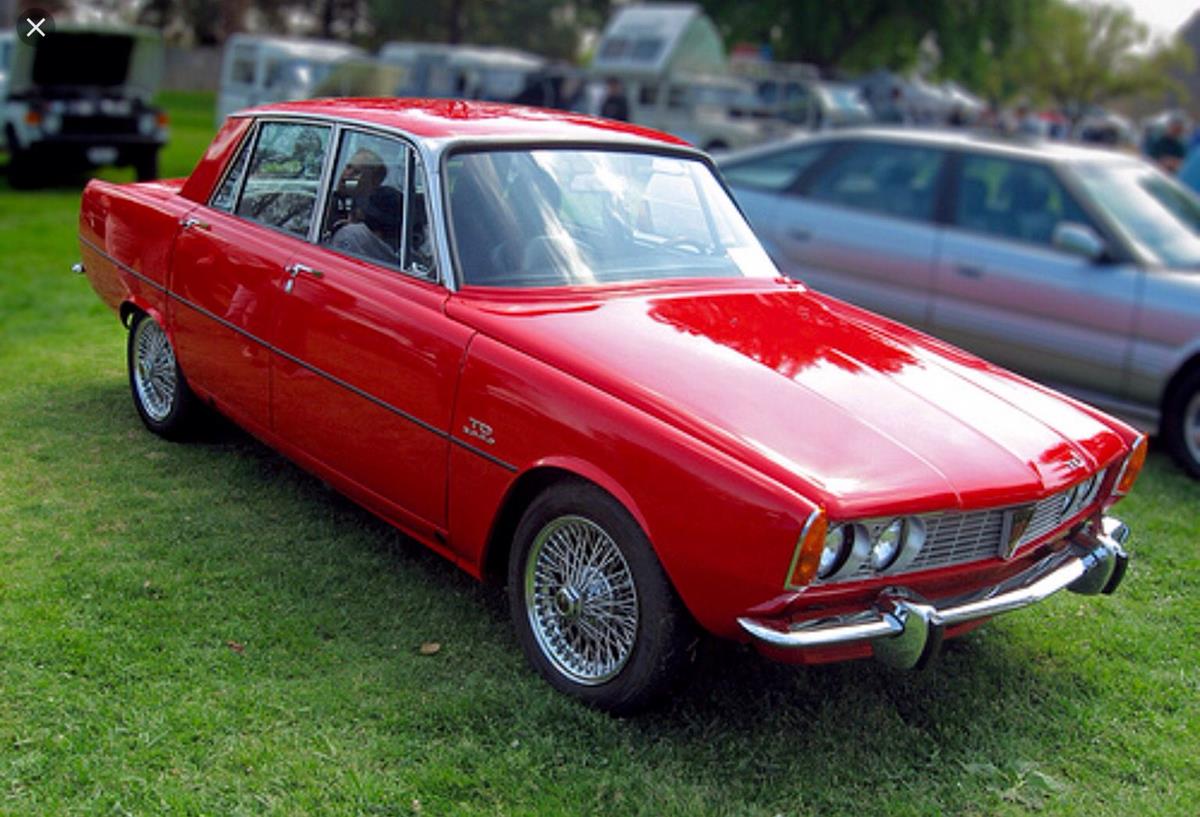
The car's primary competitor on the domestic UK market was the Triumph 2000, also released in October 1963, just one week after the P6.[7] In continental Europe, the Rover 2000 competed in the same sector as the Citroën DS which, like the initial Rover offering, was offered only with a four-cylinder engine – a situation which was resolved in the Rover when the V8 was engineered to fit into the engine bay. The Rover 2000 interior was not as spacious as those of its Triumph and Citroën rivals, especially in the back, where its sculpted two-person rear seat implied that customers wishing to accommodate three in the back of a Rover should opt for the larger and older Rover P5.
Series I
The first P6 used a 2.0 L (1,978 cc or 120.7 cu in) engine designed specifically for the P6. Although it was announced towards the end of 1963, the car had been in "pilot production" since the beginning of the year, therefore deliveries were able to begin immediately.[8] Original output was in the order of 104 bhp (78 kW). At the time the engine was unusual in having an overhead camshaft layout. The cylinder head had a perfectly flat surface, and the combustion chambers were cast into the piston crowns (sometimes known as a Heron head). With the rapid construction of motorways around the world, many of which (including those in the United Kingdom in this period) had no upper speed limits, the P6's engine was developed to be efficient, smooth and reliable when driven at high speeds for long periods. It had 'square' dimensions where the cylinder bore and stroke were the same (85.7 mm or 3.4 in) to minimise piston speeds and bearing loads, which was very unusual amongst British saloon cars: these tended to have under-square (long stroke) engines, a lingering legacy of the pre-1947 horsepower tax system and the driving conditions encountered on British roads in the pre-motorway era.
Cars that were built until 1966 are referred to as early cars. The Rover 2000 had many detailed differences that changed over the first 3 years of production. Items such as exhaust systems, gear linkages and most visibly the front valance. It had vertical slats and was curved with no extra bumps which gave the car the nick name "sharks tooth". Also on these cars the boot-shuts and the door-shuts of the base unit were painted body colour. The cars varied very slightly in appearance because radio aerials, a heated rear window and a locking fuel cap were optional extras. Early instrument panels were not made of plastic. The speedometer only went up to 110 mph and the centre console and pedals were different on later cars.

There are a number of very early cars still in existence in some form. The earliest surviving production P6 is 102 FJJ which has a good number of original panels. It is being rebuilt around a 1965 base unit. Three of the FLK cars exist 143, 145 and 149, two of which have been lovingly restored. The gold car or the 100th 2000 off the production line also survives in restored condition.
Rover later developed a derivative of the engine by fitting twin SU carburettors and a redesigned top end and marketed the revised specification vehicles as the 2000 TC. The 2000 TC was launched in March 1966 for export markets in North America and continental Europe. Limited availability of the redesigned induction manifold needed for the twin-carburetter engine was given as one reason for restricting the 2000 TC to overseas sales. The manufacturers also stated pointedly that the UK's recently introduced blanket 70 mph (113 km/h) speed limit would make the extra speed of the new car superfluous on the domestic market.[9] Fortunately for performance-oriented UK buyers, supplies of the redesigned inlet manifold must have improved and the company relented in time for the London Motor Show in October 1966 when the 2000 TC became available for the UK market. The 2000 TC prototypes had run in the Rally of Great Britain as part of their test programme. It featured a bigger starter motor and tachometer as standard and was identifiable by "TC" initials on the bodywork. The power output of the 2000 TC engine was around 124 bhp (92 kW). The standard specification engines continued in production in vehicles designated as 2000 SC models. These featured the original single SU.






























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































 LINKS E SITES IMPORTANTES
LINKS E SITES IMPORTANTES


